Table of Contents
ToggleCommon Skin Problems In India, Our skin is our body’s largest organ and acts as a protective barrier against environmental threats. However, it is also prone to various conditions, some of which can be bothersome and frustrating. From acne to eczema, skin problems can affect anyone, regardless of age or skin type. Understanding these common skin issues and how to manage them is the first step toward achieving healthy, glowing skin.
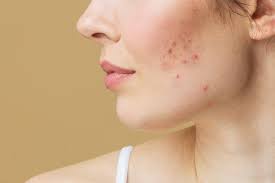
1. Acne: More Than Just Teen Trouble
Acne is one of the most common skin problems, often associated with adolescence, though it can affect people of all ages. Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria, leading to pimples, blackheads, and cysts. Hormonal changes, stress, and an overproduction of oil are typical triggers for acne. While it may seem like a temporary nuisance, untreated acne can lead to scarring and long-term skin damage.
Managing acne involves both treatment and prevention. Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids can help unclog pores and reduce inflammation. For more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe oral antibiotics or even isotretinoin. Consistent cleansing, avoiding excessive touching of the face, and using non-comedogenic products can also help prevent breakouts.
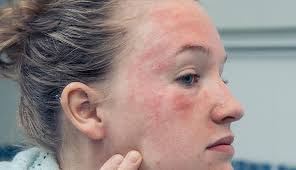
2. Eczema: An Itchy and Inflammatory Condition
Common Skin Problems In India
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition that causes the skin to become red, inflamed, and itchy. This condition often appears in childhood but can affect people of all ages. Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by various factors such as dry weather, irritants like soaps or detergents, and allergens. Stress and genetics also play a significant role in its development.
To manage eczema, it’s crucial to focus on keeping the skin moisturized. Applying fragrance-free moisturizers immediately after bathing can help lock in moisture and prevent flare-ups. In addition, using mild, soap-free cleansers, avoiding hot showers, and wearing soft, breathable fabrics can minimize irritation. For more persistent eczema, doctors may recommend topical steroids or other treatments to reduce inflammation.
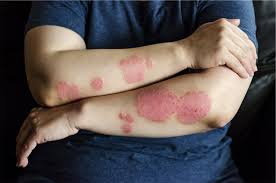
3. Psoriasis: Skin That Overproduces Cells
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition where the skin cells regenerate too quickly, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. These patches can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the scalp, elbows, and knees. Psoriasis can cause itching and discomfort, and the exact cause remains unclear, though genetics and immune system dysfunction are thought to play a role.
Managing psoriasis typically involves topical treatments, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or topical retinoids, to reduce inflammation and slow cell turnover. For more severe cases, light therapy or systemic treatments, such as oral medications or biologic injections, may be necessary. Moisturizing and avoiding triggers like stress, alcohol, and certain medications can help keep flare-ups at bay.
You said:
ChatGPT said:
Sure! A keyphrase is a group of important words that tell you what something is about.
In easy language:
A keyphrase is like a short summary made of a few words that show the main idea of a sentence, paragraph, or topic.
Examples:
For a topic like “Healthy Eating”, a keyphrase could be: 👉 “benefits of healthy food”
For a story about a dog saving a child, a keyphrase might be: 👉 “hero dog rescue”
So, when you see or hear a lot of information, a keyphrase helps you quickly understand what it’s all about.
Want help finding keyphrases from something specific?
You said:
ChatGPT said:
Sure! Here’s the meaning of slug in easy language:
🔹 What is a slug?
A slug is the last part of a web address (URL) that tells you what the page is about.
🔹 Example:
Website:https://www.example.com/how-to-make-pizza
Here, the slug is:
👉 how-to-make-pizza
🔹 In simple words:
A slug is like a name for a web page that is easy to read.
It usually uses small letters, no spaces, and hyphens between words.
🔹 Why use a slug?
It helps people understand what the page is about.
It’s good for Google and search engines (SEO).
It looks clean and simple.
Want me to show you how to make a slug from a sentence?
You said:
ChatGPT said:
Sure! Here’s a simple and informative blog on “Common Skin Problems in India” written in easy-to-understand language:
🌿 Common Skin Problems in India
India’s climate, pollution, and lifestyle can cause many skin issues. From hot summers to humid monsoons, our skin goes through a lot. Here are some of the most common skin problems people face in India, along with tips to prevent them.
1. Acne (Pimples)
Acne is very common, especially among teenagers and young adults. It happens when oil, dirt, and dead skin block the pores.
Why it happens:
Oily skin
Hormonal changes
Dust and pollution
Tips:
Wash your face twice a day
Avoid touching your face often
Use oil-free skincare products
2. Sunburn and Tanning
Strong sunlight in India can damage your skin and cause tanning or sunburn.
Why it happens:
Too much time in the sun
Not using sunscreen
Tips:
Always apply sunscreen before going out
Wear a hat or use an umbrella
Avoid going out in peak afternoon hours